SQL Database Architecture (Tables, Records, Fields)
Information in SQL-created database tables relies on the RDBMS relational concept, where system- and user-created databases store and retrieve information in a tabular format, which is organized or grouped into tables. User-created database tables are the basic building blocks of a relational database concept. Within these user-created database tables, data and information are organized and stored in a tabular format, consisting of records, known as rows, and table fields, also known as columns.
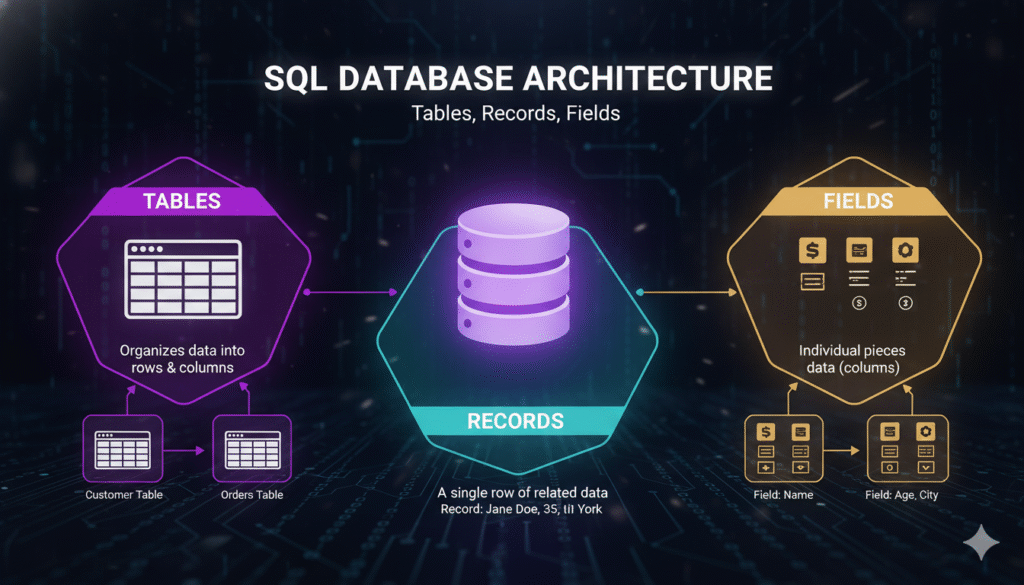
So, let’s explore the multiple elements of a SQL database.
Database Tables.
A user-generated table in a SQL database is a unique collection of custom-related data, organized or stored in a structured format using a row-and-column tabular structure format. In a relational database, each table represents a specific, unique entity. For example, a table can be named Employee, Customer, Product, or Order.
SQL Database Tables Elements.
- Table Structure – In a SQL database, each system- or user-created table has a unique name. Data and information are represented in rows and columns. Primary keys and foreign keys are used to create relationships between SQL database tables and other existing tables.
- Table Relationships – SQL database tables are connected to each other through relationships. In general, table relationship orders are defined as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many table relationship structures.
Example of a SQL database table.
Here we have a table structure format named EMPLOYEE, which represents some basic information about a company’s employees in rows and columns. The EMPLOYEE table previews something like this:
| employe_id | emp_name | emp_age | department | salary |
| 101 | Siddhi deora | 21 | Marketing | 74000 |
| 201 | Harry deora | 23 | Development | 44000 |
| 301 | Bhavshi deora | 37 | Design | 63000 |
The current table name here is employe.
Each row in the EMPLOYEE table represents an EMPLOYEE table record.
Employee table columns represent table fields such as employe_id, emp_name, emp_age, department, salary, etc.
Table Record (Row).
A table record, or row, in an SQL database table represents a single user-created digital entry displaying information. A table record row contains data and information about a particular table entity or instance. Each table record is connected to a specific entry in the table, such as an employee or customer.
Table Key.
- Primary Key – Every SQL database table has a user-defined column or set of columns created for the table, designated as the primary key. A primary key in a user-created table identifies each record in the table in a unique order.
- Foreign Key – A foreign key in a SQL database table is a column or set of columns in a table that represents the primary key of another table, managing relationships between user-created tables.
Example of a SQL table record.
Here, the Employee table represents the record of the first Employee table in the example:
employe_id emp_name emp_age department Salary
1 Siddhi Deora 21 Marketing 74000
This is a record or row in the Employee table, which represents the row information of an employee in the Marketing department, Siddhi Deora.
Table Field (Column).
A table field or column represents a specific attribute or property of the table entity represented in the table. Each Employee table field represents a specific type of row column data and information, such as text, numbers, dates, or Boolean values.
- Table Field Name – Each column in a database table has a unique column name, which represents the type of data and information the column stores and represents. For example, emp_name, emp_age, department, salary, etc.
- Table Field Data Type – Each table field in a user-defined table corresponds to a specific data type, such as INT (integer), VARCHAR (variable-length string), DATE, or DECIMAL. The data type format indicates what type of column values can be stored in that Employee table column.
Example of table fields.
Here are some column fields in the Employee table.
- employee_id – This is a unique ID identifier for each employee, typically an integer value.
- emp_name – This is the employee’s name (text) format in the Employee table.
- emp_age – This is the employee’s age (integer) format in the Employee table.
- department – This is the employee department field in the EMPLOYEE table in which the employee is working, and it is in a (text) column format.
- salary – This is the employee’s salary column field representing the (decimal) data type.
SQL Database Architecture Components.
Table Primary Key (PK).
A primary key in a SQL table is a unique identifier field value for each record in a table. A primary key in a SQL table ensures that each row in a user-created table is uniquely identified by its stored value. Remember, only one primary key can be defined per table, and it cannot contain NULL values.
A basic example of a primary key is the employe_id in the EMPLOYE table.
CREATE TABLE employe (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
emp_name VARCHAR(140),
emp_age INT,
department VARCHAR(70),
salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
Table Foreign Key (FK).
A foreign key in a SQL database table is a unique column or set of columns in a table that represents the primary key of another table. Foreign keys in SQL database tables help maintain referential integrity within a table’s column set by ensuring that relationships between the column fields of both tables are properly defined and valid.
Example – Here, a SQL database contains a Departments table and an Employees table, where each Employee table corresponds to a Department. The Department_ID field in the Employees table is defined as a foreign key, representing the ID column in the Departments table.
CREATE TABLE department (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
dep_name VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE employe (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
emp_name VARCHAR(120),
emp_age INT,
department_id INT,
salary DECIMAL(10, 2),
FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES department(id)
);
SQL Table Index.
An index in a SQL database table is a database object or method that improves the speed of data retrieval access operations on table records in an SQL database. Indexes can be created on one or more table columns to speed up SQL database table query performance, especially when querying large-volume tables.
CREATE INDEX idx_employe_name ON employe (emp_name);
Relationship type between SQL database tables.
- One-to-one relationship – In a SQL database, one record in table x is related to one record in table y.
- One-to-many relationship – In a SQL database, one record in table x is related to many records in table y.
- Many-to-many relationship – In a SQL database, many records in table x are connected to many records in table y. In a many-to-many relationship, the fields of one table are connected to many, and similarly, the fields of table y are connected to the fields of table x.


















































